- CENTOS / FEDORA / LINUX COMMANDS / LINUX DISTROS / MONITORING TOOLS / REDHAT
- 30
13 Linux Network Configuration and Troubleshooting Commands
by Ravi Saive | Published: September 24, 2012 | Last Updated: January 3, 2015
Download Your Free eBooks NOW - 10 Free Linux eBooks for Administrators | 4 Free Shell Scripting eBooks
Computers are connected in a network to exchange information or resources each other. Two or more computer connected through network media called computer network. There are number of network devices or media are involved to form computer network. Computer loaded with Linux Operating System can also be a part of network whether it is small or large network by its multitasking and multiuser natures. Maintaining of system and network up and running is a task of System / Network Administrator’s job. In this article we are going to review frequently used network configuration and troubleshoot commands in Linux.
1. ifconfig
ifconfig (interface configurator) command is use to initialize an interface, assign IP Address to interface and enable or disable interface on demand. With this command you can view IP Address andHardware / MAC address assign to interface and also MTU (Maximum transmission unit) size.
# ifconfig eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:28:FD:4C inet addr:192.168.50.2 Bcast:192.168.50.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe28:fd4c/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:6093 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:4824 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:6125302 (5.8 MiB) TX bytes:536966 (524.3 KiB) Interrupt:18 Base address:0x2000 lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1 RX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:480 (480.0 b) TX bytes:480 (480.0 b)
ifconfig with interface (eth0) command only shows specific interface details like IP Address, MAC Address etc. with -a options will display all available interface details if it is disable also.
# ifconfig eth0
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:28:FD:4C
inet addr:192.168.50.2 Bcast:192.168.50.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe28:fd4c/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:6119 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:4841 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:6127464 (5.8 MiB) TX bytes:539648 (527.0 KiB)
Interrupt:18 Base address:0x2000
Assigning IP Address and Gateway
Assigning an IP Address and Gateway to interface on the fly. The setting will be removed in case of system reboot.
# ifconfig eth0 192.168.50.5 netmask 255.255.255.0
Enable or Disable Specific Interface
To enable or disable specific Interface, we use example command as follows.
Enable eth0
# ifup eth0
Disable eth0
# ifdown eth0
Setting MTU Size
By default MTU size is 1500. We can set required MTU size with below command. Replace XXXX with size.
# ifconfig eth0 mtu XXXX
Set Interface in Promiscuous mode
Network interface only received packets belongs to that particular NIC. If you put interface inpromiscuous mode it will received all the packets. This is very useful to capture packets and analyze later. For this you may require superuser access.
# ifconfig eth0 - promisc
2. PING Command
PING (Packet INternet Groper) command is the best way to test connectivity between two nodes. Whether it is Local Area Network (LAN) or Wide Area Network (WAN). Ping use ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to communicate to other devices. You can ping host name of ip address using below command.
# ping 4.2.2.2 PING 4.2.2.2 (4.2.2.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 4.2.2.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=44 time=203 ms 64 bytes from 4.2.2.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=44 time=201 ms 64 bytes from 4.2.2.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=44 time=201 ms OR # ping www.tecmint.com PING tecmint.com (50.116.66.136) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=1 ttl=47 time=284 ms 64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=2 ttl=47 time=287 ms 64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=3 ttl=47 time=285 ms
In Linux ping command keep executing until you interrupt. Ping with -c option exit after N number of request (success or error respond).
# ping -c 5 www.tecmint.com
PING tecmint.com (50.116.66.136) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=1 ttl=47 time=285 ms
64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=2 ttl=47 time=285 ms
64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=3 ttl=47 time=285 ms
64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=4 ttl=47 time=285 ms
64 bytes from 50.116.66.136: icmp_seq=5 ttl=47 time=285 ms
--- tecmint.com ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 4295ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 285.062/285.324/285.406/0.599 ms
3. TRACEROUTE Command
traceroute is a network troubleshooting utility which shows number of hops taken to reach destination also determine packets traveling path. Below we are tracing route to global DNS server IP Address and able to reach destination also shows path of that packet is traveling.
# traceroute 4.2.2.2
traceroute to 4.2.2.2 (4.2.2.2), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 192.168.50.1 (192.168.50.1) 0.217 ms 0.624 ms 0.133 ms
2 227.18.106.27.mysipl.com (27.106.18.227) 2.343 ms 1.910 ms 1.799 ms
3 221-231-119-111.mysipl.com (111.119.231.221) 4.334 ms 4.001 ms 5.619 ms
4 10.0.0.5 (10.0.0.5) 5.386 ms 6.490 ms 6.224 ms
5 gi0-0-0.dgw1.bom2.pacific.net.in (203.123.129.25) 7.798 ms 7.614 ms 7.378 ms
6 115.113.165.49.static-mumbai.vsnl.net.in (115.113.165.49) 10.852 ms 5.389 ms 4.322 ms
7 ix-0-100.tcore1.MLV-Mumbai.as6453.net (180.87.38.5) 5.836 ms 5.590 ms 5.503 ms
8 if-9-5.tcore1.WYN-Marseille.as6453.net (80.231.217.17) 216.909 ms 198.864 ms 201.737 ms
9 if-2-2.tcore2.WYN-Marseille.as6453.net (80.231.217.2) 203.305 ms 203.141 ms 202.888 ms
10 if-5-2.tcore1.WV6-Madrid.as6453.net (80.231.200.6) 200.552 ms 202.463 ms 202.222 ms
11 if-8-2.tcore2.SV8-Highbridge.as6453.net (80.231.91.26) 205.446 ms 215.885 ms 202.867 ms
12 if-2-2.tcore1.SV8-Highbridge.as6453.net (80.231.139.2) 202.675 ms 201.540 ms 203.972 ms
13 if-6-2.tcore1.NJY-Newark.as6453.net (80.231.138.18) 203.732 ms 203.496 ms 202.951 ms
14 if-2-2.tcore2.NJY-Newark.as6453.net (66.198.70.2) 203.858 ms 203.373 ms 203.208 ms
15 66.198.111.26 (66.198.111.26) 201.093 ms 63.243.128.25 (63.243.128.25) 206.597 ms 66.198.111.26 (66.198.111.26) 204.178 ms
16 ae9.edge1.NewYork.Level3.net (4.68.62.185) 205.960 ms 205.740 ms 205.487 ms
17 vlan51.ebr1.NewYork2.Level3.net (4.69.138.222) 203.867 ms vlan52.ebr2.NewYork2.Level3.net (4.69.138.254) 202.850 ms vlan51.ebr1.NewYork2.Level3.net (4.69.138.222) 202.351 ms
18 ae-6-6.ebr2.NewYork1.Level3.net (4.69.141.21) 201.771 ms 201.185 ms 201.120 ms
19 ae-81-81.csw3.NewYork1.Level3.net (4.69.134.74) 202.407 ms 201.479 ms ae-92-92.csw4.NewYork1.Level3.net (4.69.148.46) 208.145 ms
20 ae-2-70.edge2.NewYork1.Level3.net (4.69.155.80) 200.572 ms ae-4-90.edge2.NewYork1.Level3.net (4.69.155.208) 200.402 ms ae-1-60.edge2.NewYork1.Level3.net (4.69.155.16) 203.573 ms
21 b.resolvers.Level3.net (4.2.2.2) 199.725 ms 199.190 ms 202.488 ms
4. NETSTAT Command
Netstat (Network Statistic) command display connection info, routing table information etc. To displays routing table information use option as -r.
# netstat -r
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
192.168.50.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
default 192.168.50.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
For more examples of Netstat Command, please read our earlier article on 20 Netstat Command Examples in Linux.
5. DIG Command
Dig (domain information groper) query DNS related information like A Record, CNAME, MX Record etc. This command mainly use to troubleshoot DNS related query.
# dig www.tecmint.com; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.10.rc1.el6 <<>> www.tecmint.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<
For more examples of Dig Command, please read the article on 10 Linux Dig Commands to Query DNS.
6. NSLOOKUP Command
nslookup command also use to find out DNS related query. The following examples shows A Record (IP Address) of tecmint.com.
# nslookup www.tecmint.com
Server: 4.2.2.2
Address: 4.2.2.2#53
Non-authoritative answer:
www.tecmint.com canonical name = tecmint.com.
Name: tecmint.com
Address: 50.116.66.136
For more NSLOOKUP Command, read the article on 8 Linux Nslookup Command Examples.
7. ROUTE Command
route command also shows and manipulate ip routing table. To see default routing table in Linux, type the following command.
# route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.50.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth0
default 192.168.50.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
Adding, deleting routes and default Gateway with following commands.
Route Adding
# route add -net 10.10.10.0/24 gw 192.168.0.1
Route Deleting
# route del -net 10.10.10.0/24 gw 192.168.0.1
Adding default Gateway
# route add default gw 192.168.0.1
8. HOST Command
host command to find name to IP or IP to name in IPv4 or IPv6 and also query DNS records.
# host www.google.com
www.google.com has address 173.194.38.180
www.google.com has address 173.194.38.176
www.google.com has address 173.194.38.177
www.google.com has address 173.194.38.178
www.google.com has address 173.194.38.179
www.google.com has IPv6 address 2404:6800:4003:802::1014
Using -t option we can find out DNS Resource Records like CNAME, NS, MX, SOA etc.
# host -t CNAME www.redhat.com
www.redhat.com is an alias for wildcard.redhat.com.edgekey.net.
9. ARP Command
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is useful to view / add the contents of the kernel’s ARP tables. To see default table use the command as.
# arp -e
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
192.168.50.1 ether 00:50:56:c0:00:08 C eth0
10. ETHTOOL Command
ethtool is a replacement of mii-tool. It is to view, setting speed and duplex of your Network Interface Card (NIC). You can set duplex permanently in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 withETHTOOL_OPTS variable.
# ethtool eth0
Settings for eth0:
Current message level: 0x00000007 (7)
Link detected: yes
11. IWCONFIG Command
iwconfig command in Linux is use to configure a wireless network interface. You can see and set the basic Wi-Fi details like SSID channel and encryption. You can refer man page of iwconfig to know more.
# iwconfig [interface]
12. HOSTNAME Command
hostname is to identify in a network. Execute hostname command to see the hostname of your box. You can set hostname permanently in /etc/sysconfig/network. Need to reboot box once set a proper hostname.
# hostname
tecmint.com
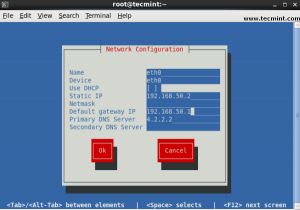
13. GUI tool system-config-network
Type system-config-network in command prompt to configure network setting and you will get niceGraphical User Interface (GUI) which may also use to configure IP Address, Gateway, DNS etc. as shown below image.
# system-config-network
This article can be useful for day to day use of Linux Network administrator in Linux / Unix-like operating system. Kindly share through our comment box if we missed out.
If you have any questions or problems regarding this article and want help within 24 Hours? Ask Now
Support TecMint: Did you find this tutorial helpful?. Please help to keep it alive by donating. Every cent counts! - Donate Now
Ravi Saive
Simple Word a Computer Geek and Linux Guru who loves to share tricks and tips on Internet. Most Of My Servers runs on Open Source Platform called Linux.
Your name can also be listed here. Got a tip? Submit it here to become an TecMint author.
Receive Your Free Complimentary eBook NOW! - 4 Promising Linux Distros To Look Forward To In 2015
- NEXT STORYHow to Use Remote Desktop (rdesktop) in Redhat/Fedora/CentOS
- PREVIOUS STORYInstall Memcached (Caching Server) on RHEL/CentOS 6.3/5.8 and Fedora 17-12
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE...
30 RESPONSES
LEAVE A REPLY
DOWNLOAD FREE LINUX EBOOKS
- Complete Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet
- The GNU/Linux Advanced Administration Guide
- Securing & Optimizing Linux Servers
- Linux Patch Management: Keeping Linux Up To Date
- Introduction to Linux – A Hands on Guide
- Understanding the Linux® Virtual Memory Manager
- Linux Bible – Packed with Updates and Exercises
- A Newbie’s Getting Started Guide to Linux
- Linux from Scratch – Create Your Own Linux OS
- Linux Shell Scripting Cookbook, Second Edition
- Securing & Optimizing Linux: The Hacking Solution
- User Mode Linux – Understanding and Administration



Used for system network troubleshooting..